In an era where digital services are a fundamental part of everyday life, users are often required to log in to a multitude of websites and applications.
Managing numerous usernames, passwords, and security questions can become overwhelming, not to mention risky, so the need for efficient, secure, and scalable login solutions is more important than ever.
My name’s Peter Fernandez, and in this article, I’m going to share how, for business and consumers alike, Single Sign-On (SSO) helps make this a reality as part of CIAM Solution Architecture.
What is SSO?
Once the province of enterprise environments, SSO in a CIAM context is an authentication process that allows users to seamlessly access multiple applications or services with login credentials associated with a wide variety of digital identities (e.g. Social, Federation, etc).
With the growing number of commercial B2C and B2B SaaS applications, SSO has now become a crucial tool for streamlining consumer authentication while improving security and the user experience. SSO provides an independent authentication that enables a user to log in once and gain access to multiple applications or services without needing to repeatedly enter their credentials.
How Does SSO Work?
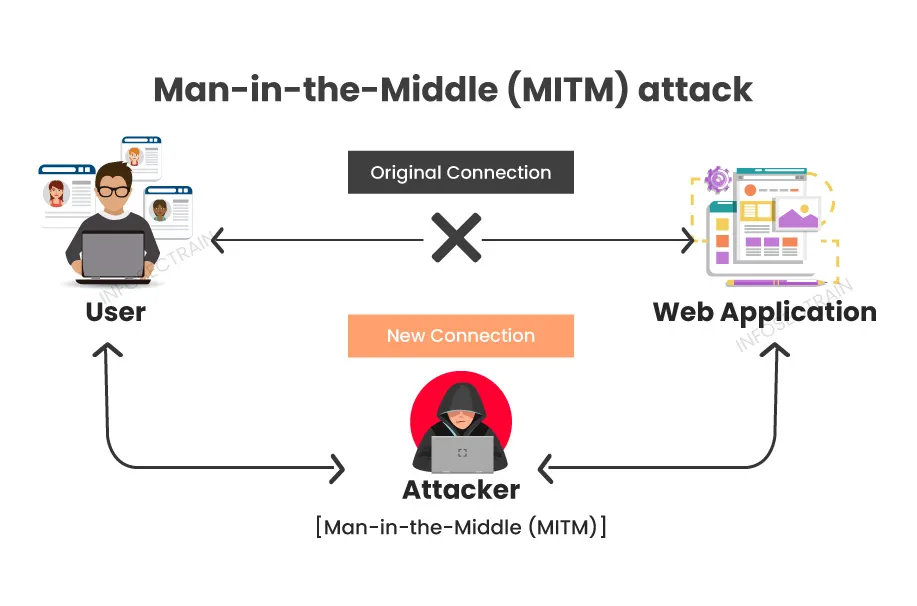
SSO works through the use of an application-independent identity provider (IdP) service that: (a) validates a user’s credentials, (b) establishes a secure authenticated context, and (c) generates one or more authentication artefacts.
I recently came across a great post on LinkedIn that illustrates the rudimentary aspects of this in more detail, and where, in a CIAM context, the verification of credentials can also include verification from an upstream IdP:
The established security context is used across all linked applications — also known as Service Providers or Relying Parties, depending on which protocols you use — allowing the user access without requiring them to interactively log in repeatedly.
SSO can work across various B2C and B2B SaaS platforms, ranging from enterprise software suites to cloud-based application services, simplifying and streamlining the authentication process for a user, whilst at the same time enabling enhanced security and reducing administrative overhead.
Improved User Experience
One of the most significant benefits of implementing SSO is the improved user experience. Traditionally speaking, SSO was predominantly used in corporate IAM environments, where employees no longer needed to remember multiple usernames and passwords, nor interactively enter them for each application they use — instead only needing to remember one set of login credentials to access a wide variety of services.
Within a CIAM environment, consumer users can benefit too. By utilising SSO, customers can make use of multiple authentication methods — including Social, (Enterprise) Federation and Passkeys — which can then all be linked to the same user account in a process known as Account Linking (crucial for delivering a secure and smooth experience that’s consistent no matter how a user chooses to log in).
If you’ve ever used a site where your profile changes depending on whether you’ve logged in using UserID and Password, or some Social connection like Facebook, you’ll know exactly what I mean!
The simplification SSO brings is now valuable in various ways, not just for organisations that provide employees with access to several internal applications. Third-party B2B SaaS applications deployed for internal use, as well as for B2C consumers who interact with multiple platforms, can now benefit from ease of use as well as a consistent experience.
With SSO, users can seamlessly move between applications without interruptions, no matter which authentication protocol the application uses (i.e. SAML or OIDC). This makes the entire login process faster and more intuitive, reducing friction, saving time, resulting in less frustration, and enhancing overall productivity for both businesses and individuals.
Enhanced Security
While SSO is often associated with convenience, it also provides significant security benefits. Here are a few ways SSO improves the security landscape:
- Easier User Monitoring and Auditing: Because user access is managed centrally, it’s easier to monitor login attempts, track activities, and identify suspicious behaviour across applications. In the case of a potential security breach, access can quickly be disabled or suspicious login patterns investigated from one central location.
- Reduced Password Fatigue: With fewer passwords to remember, users are less likely to reuse passwords across multiple accounts (a common vulnerability in digital security scenarios). SSO also encourages the use of stronger, more secure credentials by minimising the need to manage multiple passwords…even doing away with them altogether!
- Centralised Authentication: SSO typically predicates the use of an application-independent IdP, which in turn allows the enforcement of uniform security policies across all integrated applications. For example, strong passwords can be required, multi-factor authentication (MFA) implemented, or specific expiration periods for user sessions defined, all in one place. By consolidating these, SSO helps ensure that all services adhere to the same high-security standards.
- Decreased Risk of Attack: When users have fewer passwords to remember (or even no password at all), the likelihood of falling victim to phishing attacks or credential stuffing attacks is reduced. Further, if an attacker is unable to obtain a user’s first-factor credentials in the first place, either because the user is encouraged to use Social authentication, or a Passkey alternative, their ability to gain access to the multiple accounts a user may have across the various services is greatly reduced
Time and Cost Saving
Implementing SSO can lead to significant time and cost savings, too:
- Reduced Support Costs: Password-related issues are one of the most common sources of IT support tickets. Users often forget passwords, require password resets, or face login issues that prevent them from accessing critical applications. With SSO, the reduction in password-related support requests frees IT teams to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Faster Onboarding and Offboarding: Onboarding new users can be a time-consuming process, particularly with employees (where it can involve creating and managing multiple sets of credentials across different applications). With SSO, all necessary tools can be accessed with one login, streamlining the process. Similarly, when someone leaves, their access can be disabled, resulting in SSO session termination across all linked services and enhancing security by simplifying the process of offboarding.
- Operational Efficiency: SSO eliminates the need for repetitive login procedures, saving time and increasing efficiency. When users don’t have to spend time re-entering passwords or managing different accounts, they can focus on what they want/need to do. Additionally, with seamless access to all necessary applications, employees can work more effectively without experiencing bottlenecks caused by inefficient login systems.
Scalability and Flexibility
As systems grow, so too does their complexity. Companies, for instance, often adopt multiple (B2B SaaS) applications, tools, and platforms to meet their needs, whether it’s for collaboration, project management, data storage, or customer relationship management (CRM). Consumer (B2C) platforms can end up leveraging multiple integrations. All this means the need for a scalable, flexible authentication solution becomes paramount.
By predicating the use of an application-independent IdP, SSO makes it easier to scale operations by providing a flexible authentication model that can accommodate an expanding range of applications and application services. Whether adding new cloud capabilities, third-party integrations, or expanding globally, SSO allows seamless integration without needing new login credentials for each addition.
Furthermore, SSO allows centralised control over user access and data security, making it easier to add or remove applications from a system as needs evolve.
Compliance with Regulatory Standards
Many industries are subject to strict regulatory standards for data protection and privacy, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS).
These regulations often require organisations to ensure that only authorised users have access to sensitive data, maintain secure login processes, and implement strong authentication methods.
SSO helps businesses comply with these regulations by allowing them to manage access to critical resources in a standardised and secure way. Administrators can enforce uniform security policies, track user activities, and generate audit trails, ensuring that the organization meets compliance requirements and reduces the risk of penalties.
Integrating Third-Party Applications
In today’s interconnected world, businesses often rely on third-party B2B SaaS to extend the functionality of their applications. These could include tools for marketing, customer support, document collaboration, or social media management. Managing separate login credentials for each service can quickly become cumbersome and does not effectively scale.
SSO allows businesses to integrate third-party applications into their ecosystem with ease. Many third-party vendors offer SSO support via standards like OIDC or SAML, allowing businesses to provide a unified authentication experience across their entire software suite, including external services.
By integrating third-party applications through SSO, businesses reduce the administrative burden of managing multiple credentials and offer users a seamless experience when using both internal and external tools.
Better User Adoption and Engagement
A smoother, more convenient login experience encourages user adoption and engagement. When users can easily access the applications they need without dealing with frustrating login procedures, they are more likely to embrace the tools offered by a business or platform. This can be especially important for consumer-facing platforms, where user satisfaction and retention are critical.






















Leave a Reply