In today’s increasingly digital world, protecting sensitive customer data while ensuring seamless access to services is a top priority for any business. Customer Identity and Access Management (a.k.a. CIAM) is a framework designed to handle customer identities and their access to digital services and is a crucial component of any modern cybersecurity strategy.
My name’s Peter Fernandez, and in this article, I’m going to be discussing how integrating CIAM into your B2C/B2B SaaS solution not only provides secure access but also helps you deliver personalised, efficient, and user-friendly experiences.
What is CIAM?
CIAM refers to a set of technologies, processes, policies and procedures that enable customer identities and access rights to be managed safely and securely.
Unlike traditional Identity and Access Management (IAM) systems, often referred to as Workforce IAM (primarily focusing on the management of identities and access permissions for internal employees), CIAM is specifically tailored for consumer-facing applications and services.
At its core, CIAM is essentially concerned with two primary goals:
- Customer Identity: CIAM ensures that the identity of your customers is securely authenticated and verified during digital interactions, typically using first-factor and multi-factor (MFA) authentication mechanisms.
- Customer Access: CIAM is also pivotal when it comes to controlling the access your customers have to the various services you provide, ensuring that users and applications can only access the information they are authorised to.
CIAM brings value to any B2C and B2B SaaS solution but is particularly important in scenarios that require the secure management of customer data and interactions (such as in e-commerce, banking, healthcare, entertainment and anything with a commercial aspect) at scale.
Key Components
A well-implemented CIAM solution typically comprises several key components, working together to provide robust identity and access management. These components largely fall into the following categories:
- Authentication: Authentication refers to the process of validating the identity of customers when they log in or register for services. CIAM solutions should support multiple authentication mechanisms, such as traditional UserID and Password, as well as more advanced methods, including Passkeys, MFA, and passwordless login. Learn more about Authentication at Discover/CIAM/Authenticate, including:
- Identity Federation: enabling customers to use their existing credentials from external Enterprise and Social identity providers (such as Google, Facebook, or LinkedIn) to authenticate via third-party platforms or websites. This eliminates the need for customers to remember multiple usernames and passwords, promoting convenience and security at scale.
- Single Sign-On (SSO): allows customers to log in once and gain access to multiple applications or services without needing to re-enter their credentials. This enhances the user experience by reducing friction while ensuring secure and seamless access to connected services.
- Authorization: Authorization ensures that customers can only access the specific resources and services they are permitted to. CIAM systems typically use access control mechanisms (such as ReBAC, RBAC or ABAC) to assign rights based on user relationships, roles or attributes, ensuring that sensitive data is protected. More about Authorization can be found at Discover/CIAM/Authorize, which includes:
- Consent: Managing customer consent for data collection and processing is a crucial aspect of CIAM, especially in light of regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). CIAM solutions help businesses collect, track, and manage consent for various data processing activities, ensuring compliance with privacy laws.
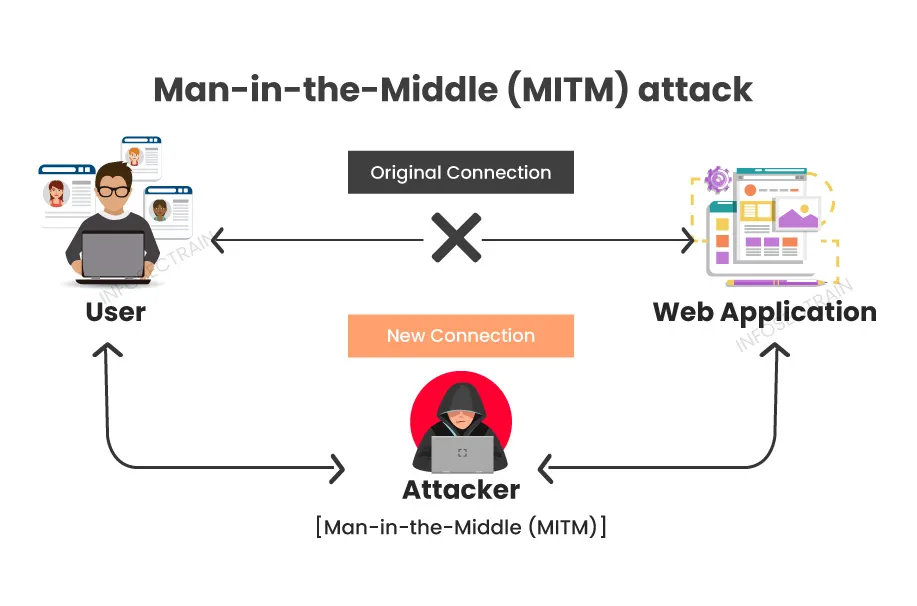
- Protection: Protecting personal data is just as important as securing customer identity and is an important aspect of doing business in a modern commercial environment. So, mechanisms for mitigating the likes of Phishing, Brute Force attacks, etc., are critical for safeguarding your users and their precious information. For more, see Discover/CIAM/Protect, which also includes:
- Analytics and Reporting: CIAM systems provide insights into user behaviour, login patterns, and access requests. This helps organisations monitor for suspicious activity, detect potential security breaches, and optimise the user experience based on data-driven insights.
- Management: Together with self-service capabilities, APIs that complement configuration and control via an Administrative Portal make it easy to integrate operational management and deployment with existing systems. Uncover more at Discover/CIAM/Manage, which includes:
- Profile Management: CIAM allows customers to create and manage their profiles by providing essential information such as their name, email address, date of birth, and more, in many cases, making use of frictionless techniques such as progressive profiling, too. It also includes features for editing and updating customer information securely and safely, often in a self-service manner.
- Self-Service: CIAM platforms typically offer self-service portals where customers can manage their own accounts, reset passwords, update contact details, or change preferences. This minimises the need for customer support whilst improving user satisfaction.
Benefits
CIAM offers numerous benefits to teams that build B2C or B2B style SaaS applications, making it an essential part of modern consumer software development. Such benefits include:
- Enhanced Security: By implementing robust authentication and authorization protocols, CIAM helps protect customer data from unauthorised access, reducing the risk of data breaches. Features such as MFA and advanced threat detection further enhance security, especially when dealing with sensitive information.
- Improved User Experience: CIAM solutions provide a frictionless experience for customers by enabling features like Single Sign-On (SSO), Social login options, and self-service account management. This convenience leads to higher customer satisfaction, increased retention rates, and better engagement.
- Personalisation: With access to detailed customer data (such as preferences, purchase history, and behaviour), CIAM allows businesses to deliver personalised experiences. Personalised recommendations, targeted marketing, and customised content are all made possible through effective customer identity and access management.
- Regulatory Compliance: In many industries, ensuring compliance with regulations such as the GDPR and CCPA is essential. CIAM platforms help businesses manage user consent, data access, and privacy preferences in a manner that complies with data protection laws, reducing the risk of costly fines.
- Scalability: As businesses grow, so does the volume of customer data and interactions. CIAM solutions are designed to scale with the business, handling increasing user numbers and access requests without compromising performance or security.
- Brand Trust: By providing a secure and seamless experience, businesses can build trust with customers. Customers are more likely to engage with and return to services they trust, which can lead to greater brand loyalty and long-term success.
- Cost Savings: By automating identity management processes, including registration, authentication, and password recovery, businesses can reduce the strain on customer support teams. This results in cost savings and improved operational efficiency.
Challenges
However, despite the many benefits, implementing CIAM is not without challenges. Some of the most common challenges include:
- Complex Integration: Integrating CIAM systems with existing legacy systems, customer databases, and third-party services can be complex and time-consuming. Proper planning and technical expertise are required to ensure smooth integration.
- Data Privacy Concerns: Managing customer data securely and ensuring that privacy laws are adhered to is a major challenge. Organisations need to invest in robust security measures and data governance practices to ensure that customer information is protected.
- User Adoption: While CIAM solutions aim to simplify the user experience, getting customers to adopt new authentication methods, such as MFA or biometric login, can be a hurdle. Some customers may find these new methods inconvenient or difficult to use, which can lead to resistance.
- Cost of Implementation: Implementing a CIAM solution requires significant investment in terms of technology, training, and ongoing maintenance. Small businesses or startups may find the cost prohibitive, especially when compared to other security solutions.
Purchasing a third-party SaaS solution, or leveraging open-source implementation, is often preferable (and recommended) over rolling your own, and you can read more about that in my article entitled:






















Leave a Reply